88-LC0-36FH-M Overview
Cisco 8000 Series Line Cards 88-LC0-36FH-M,Cisco 8800 36x400GbE QSFP56-DD Line Card with MACsec based on Q200 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes
Cisco 8800 Series line cards
The Cisco 8800 Series modular platform supports six different 100GbE, 400GbE, and 800G line cards. The line cards utilize multiple Cisco Silicon One forwarding ASICs to achieve high performance and bandwidth with line rate forwarding. All ports on all six-line cards support different breakout options for 200 GbE, 100GbE, 50GbE, 40GbE, and 10GbE
Cisco 8800 Series line card options
| Line Cards | Bandwidth | Silicon | 100GbE Ports | 400GbE Ports | 800G Ports
(2x 400GbE) |
MACsec |
| 8800-LC-48H | 4.8 Tbps | Q100 | 48 | – | – | Yes |
| 88-LC0-34H14FH | 9 Tbps | Q200 | 34 | 14 | – | 16x 100GbE ports |
| 8800-LC-36FH | 14.4 Tbps | Q100 | – | 36 | – | No |
| 88-LC0-36FH | 14.4 Tbps | Q200 | – | 36 | – | No |
| 88-LC0-36FH-M | 14.4 Tbps | Q200 | – | 36 | – | Yes |
| 88-LC1-36EH | 28.8 Tbps | P100 | – | – | 36 | No |
There are six different line cards supported on all 8800 modular chassis.
The 48-port QSFP28 100GbE line card provides 4.8 Tbps of throughput with MACsec support on all ports. It also supports QSFP+ optics for 10G and 40G compatibility.

Figure 12.
48-port QSFP28 100GbE line card
The two variants of 36-port QSFP56-DD 400GbE line cards are based on Q100 and Q200 silicon chips. Each line card provides 14.4 Tbps via 36 QSFP56-DD front-panel ports.

Figure 13.
36-port QSFP56-DD 400GbE line card
There is also a Q200-based, MACsec-capable, 36-port QSFP56-DD 400GbE line card that provides 14.4 Tbps of throughput with line rate MACsec on all ports.
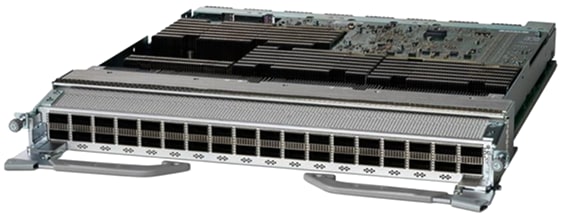
Figure 14.
36-port QSFP56-DD 400GbE line card with MACsec
The 36-port QSFP-DD800 800G line card provides 28.8 Tbps of throughput. Each 800G port can be used as 2x400GbE ethernet or 8x100GbE ethernet.

Figure 15.
36-port QSFP-DD800 800G line card
In addition, there is a combo card that provides 34 – QSFP28 ports and 14 – QSFP56-DD ports. It offers customers the ability to smoothly transition from 100G to 400G. For additional flexibility, this card supports MACsec on 16 of the 100GbE ports.
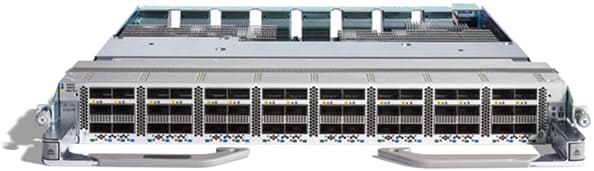
Figure 16.
34 – port QSFP28 100GbE and 14 – port QSFP56-DD 400GbE
Cisco 8000 Series
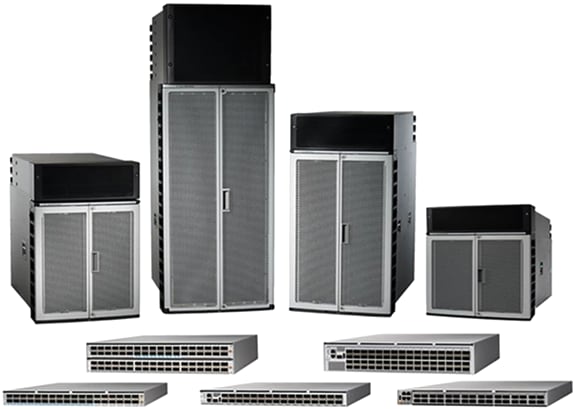

Figure 1.
Cisco 8000 Series routers
High-performance networking systems have historically been divided into routing or switching classes, with distinct hardware and software. Over time, this distinction has become less pronounced. This convergence has occurred with the evolution of feature-rich switching chips and routing chips that balance traditional Service Provider (SP)–class capabilities with many benefits of switching Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs).
Cisco®8000 Series routers complete this journey. They deliver provider-class routing functionality at unmatched density, performance, and power. This enables Cisco 8000 Series to be deployed into an unprecedented range of routing roles – all supported with a single ASIC architecture and operating system – thus streamlining qualification, deployment, and operations.
The Cisco 8000 Series combines the revolutionary Cisco Silicon One™, IOS XR®software, and a set of clean sheet chassis to deliver a breakthrough in high-performance routers. The 8000 Series comprises a full range of feature-rich, highly scalable, deep-buffered, on-chip High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and 400 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE)-optimized routers ranging from 10.8 to 25.6 Tbps in a 1 RU footprint. It is also available in an industry leading, rack-mountable modular system capable of 518.4 Tbps of full-duplex, line rate forwarding.
The Cisco 8000 Series includes two distinct router architectures that both utilize the Cisco Silicon One ASICs. The 8800 Series provides the highest bandwidth via modular chassis with a redundant control plane and switch fabric. The 8800 Series includes the Cisco 8804, 8808, 8812, and 8818. These chassis deliver up to 28.8 Tbps per line card via 100, 400, and 2x400GbE (800G) ports.
The Cisco 8100 and 8200 Series utilize Cisco’s Router-on-Chip (RoC) architecture to deliver full routing functionality with a single ASIC per router. Both support the full routing feature set, but the 8200 has deep buffers and expanded forwarding tables, while the 8100 Series is targeted for data center applications with lower buffering and forwarding table scale requirements.
The RoC architecture is distinguished from System-on-Chip (SoC) switches by supporting large forwarding tables, deep buffers, more flexible packet operations, and enhanced programmability. The Cisco 8100 and 8200 provide up to 25.6 Tbps of network bandwidth with lower power than similar systems.
Cisco 8000 Series Routers Datasheet
Cisco 8000 Series Line Cards ordering information
| Product Name | Product Description |
| 8800-LC-48H | Cisco 8800 48x100GbE QSFP28 Line Card based on Q100 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes |
| 88-LC0-34H14FH | Cisco 8800 34x100GbE QSFP28 and 14x400GbE QSFP56-DD Line Card based on Q200 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes |
| 8800-LC-36FH | Cisco 8800 36x400GbE QSFP56-DD Line Card based on Q100 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes |
| 88-LC0-36FH | Cisco 8800 36x400GbE QSFP56-DD Line Card based on Q200 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes |
| 88-LC0-36FH-M | Cisco 8800 36x400GbE QSFP56-DD Line Card with MACsec based on Q200 Silicon with 56Gb Serdes |
| 88-LC1-36EH | Cisco 8800 36x800G QSFP-DD800 Line Card based on P100 Silicon with 112Gb Serdes |
 IT Network Equipment Supplier
IT Network Equipment Supplier


 What’s your advantages?
What’s your advantages? We are premium selected partner of Cisco. we are a professional supplier in network equipment field more than five years. We supply original products with good price to customers. We have professional sales team provide 24 hours free-consulting, and we also have professional technical team and after-sales department.
We are premium selected partner of Cisco. we are a professional supplier in network equipment field more than five years. We supply original products with good price to customers. We have professional sales team provide 24 hours free-consulting, and we also have professional technical team and after-sales department.


















